Exploring Dominant Culture: Shaping Society, Fostering Pluralism, And Bridging Cultural Divides
Dominant culture refers to the prevailing set of beliefs, values, norms, and practices that shape the social, political, and economic landscape of a society. It influences the way individuals perceive the world and interact with each other. Understanding dominant culture is crucial for fostering tolerance, inclusivity, and cultural harmony. It encompasses cultural hegemony, where dominant cultural values are normalized, and assimilation, where minorities adapt to these norms. Dominant culture coexists with minority cultures, which face pressures to conform while also preserving their unique identities. Cultural pluralism advocates for the coexistence of diverse cultures, while multiculturalism embraces these differences. Intercultural communication bridges cultural gaps, promoting understanding and respect. Recognizing and valuing cultural diversity is essential for building a harmonious society that celebrates the richness of human experiences.
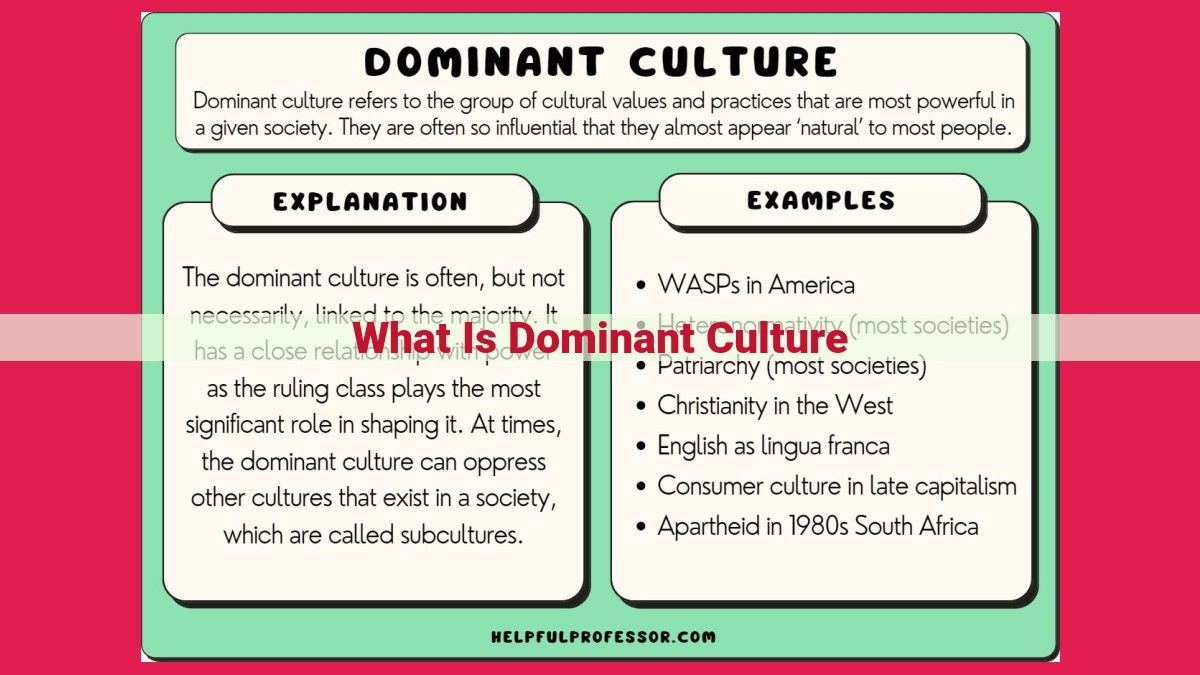
Dominant Culture: Understanding Its Role and Significance
In every society, there exists a dominant culture, a set of beliefs, values, norms, and practices that shape the prevailing worldview and influence the lives of its members. This culture holds a prominent position, shaping the social, economic, and political landscape.
Defining Dominant Culture
A dominant culture is the culture of the majority group in society. It reflects the values, beliefs, and practices that are widely shared and accepted within that group. This culture often exerts a significant influence on other minority cultures, shaping their experiences and interactions.
Importance of Understanding Dominant Culture
Understanding dominant culture is crucial for several reasons.
- The prevailing norms and values that shape societal behavior
- The power dynamics and social hierarchies within society
- The challenges and opportunities faced by minority groups
- How individuals navigate cultural differences and maintain their identities
Ties to Social Structure
Dominant culture is closely intertwined with the social structure of a society. It reinforces and perpetuates existing power structures, shaping access to resources, opportunities, and social status. Understanding this dynamic is essential for promoting social justice and equity.
Dominant Culture's Influence: Cultural Hegemony and Assimilation
Cultural Hegemony: Shaping Beliefs and Values
Dominant culture exerts its influence through a subtle yet powerful mechanism known as cultural hegemony. This process subtly shapes the beliefs, values, and norms of a society, often without individuals consciously realizing it. The hegemonic culture permeates various aspects of life, including media, education, and institutions, subtly reinforcing its worldview and ideologies.
Assimilation: Conforming to Dominant Norms
Assimilation is the process by which minority cultures *adopt the dominant cultural norms*, often at the expense of their own traditions and values. This occurs when individuals from minority groups seek to conform to the prevailing societal expectations and standards. While assimilation can lead to greater social acceptance, it can also result in the marginalization or even *loss of minority cultures*.
Minority Culture and Its Interaction with Dominant Culture
- Define minority culture and its characteristics
- Examine the impact of cultural assimilation on minority cultures
Minority Culture and Its Interaction with Dominant Culture
In the tapestry of society, where various cultures intertwine, minority cultures emerge as unique threads that contribute to the overall vibrant and diverse fabric. Defined as cultural groups that differ from and possess less power than the dominant culture, minority cultures often leave a profound mark on the social landscape.
Characteristics of Minority Cultures
Minority cultures often share distinct characteristics that set them apart from the dominant culture. These may include:
- Distinct language, traditions, and customs: Minority cultures often have their own language, passed down through generations, as well as unique traditions and customs that shape their way of life.
- Strong sense of community: Minority cultures frequently foster a close-knit sense of community, where individuals share a common identity and support system.
- Resilience and adaptability: Despite facing challenges, minority cultures exhibit remarkable resilience and adaptability, preserving their heritage while navigating the complexities of a dominant culture.
Impact of Cultural Assimilation on Minority Cultures
As minority cultures interact with the dominant culture, a process of cultural assimilation often occurs. This involves the adoption of dominant cultural values, beliefs, and behaviors by minority individuals. While assimilation can bring about benefits such as access to education and economic opportunities, it can also have significant consequences for minority cultures.
- Loss of cultural identity: Assimilation can lead to the gradual erosion of cultural identity as minority individuals adopt dominant cultural norms.
- Cultural conflicts: Conflicting cultural values between the dominant and minority cultures can create tensions and challenges for individuals.
- Intergenerational gaps: Assimilation may create a divide between older and younger generations within minority communities, as younger individuals embrace dominant cultural influences while elders strive to preserve traditions.
Cultural Pluralism: Harmony Amidst Diversity
Cultural pluralism is a fundamental concept that advocates for the coexistence of diverse cultures within a society. It recognizes that different cultural groups maintain their unique beliefs, values, practices, and traditions while also being part of a broader society. This coexistence allows for a vibrant and harmonious social fabric.
In contrast to cultural hegemony, where one culture dominates and suppresses others, cultural pluralism promotes equality and respect for all cultures. It allows minority cultures to preserve their identities and flourish, fostering a sense of belonging and empowerment within diverse communities.
Furthermore, cultural pluralism differentiates itself from cultural assimilation, where minority cultures adopt the norms and values of the dominant culture, often at the expense of their own. Cultural pluralism encourages the preservation of cultural diversity, recognizing that each culture contributes unique perspectives and values to society.
Multiculturalism: Embracing the Tapestry of Cultural Diversity
In the vibrant tapestry of our world, the intersection of cultures paints a rich and diverse landscape. Multiculturalism emerges as a beacon of inclusivity, recognizing and honoring the coexistence of distinct cultural identities. Its goal is to foster a harmonious society where individuals from various backgrounds feel valued and respected.
Comparing Multiculturalism with Cultural Hegemony and Cultural Pluralism
Multiculturalism stands in stark contrast to cultural hegemony, the dominance of a single culture that marginalizes others. Unlike cultural pluralism, which recognizes cultural differences while maintaining separate identities, multiculturalism actively promotes the intermingling and exchange of cultural practices. It encourages individuals to embrace the richness of their own heritage while simultaneously exploring and appreciating the traditions of others.
Within multicultural societies, individuals have the freedom to express their cultural identities through language, food, art, and customs. Public policies often support initiatives such as bilingual education and multicultural festivals, fostering a sense of belonging and empowerment for all. By celebrating diversity, multiculturalism creates a dynamic and vibrant social fabric where everyone's voice is heard and valued.
Intercultural Communication: Bridging Cultural Gaps
In an increasingly interconnected world, understanding and respecting cultural diversity is paramount. Intercultural communication plays a vital role in fostering harmonious relationships among individuals from different cultural backgrounds. It involves the exchange of information, ideas, and emotions between people of different cultures, enabling them to bridge cultural gaps and build mutual understanding.
Intercultural communication is essential for a diverse society. It promotes tolerance, reduces stereotyping, and facilitates cooperation. By engaging in intercultural dialogue, we gain deeper insights into different perspectives, worldviews, and ways of life. This fosters empathy and breaks down barriers that divide us.
Moreover, intercultural communication is intertwined with multiculturalism, which values and promotes the preservation of cultural diversity within a society. While cultural hegemony and cultural assimilation seek to impose a dominant culture over others, multiculturalism embraces the richness and diversity of all cultures. Intercultural communication is the key to fostering a truly multicultural society where people from all backgrounds can thrive and contribute.
Related Topics:
- Exercise Regression: Optimize Your Fitness Journey Despite Limitations
- Ultimate Guide To Combating Gang Stalking: Empowering Yourself With Knowledge And Protection
- How To Treat Orange Tongue: Causes, Remedies, And Prevention
- Comprehensive Guide To Measuring Glutes: Detailed Instructions And Techniques
- Power Vs. Energy: Understanding The Transfer And Capacity Of Work