Population Dynamics And Community Structure: Unraveling The Complexity Of Ecosystems
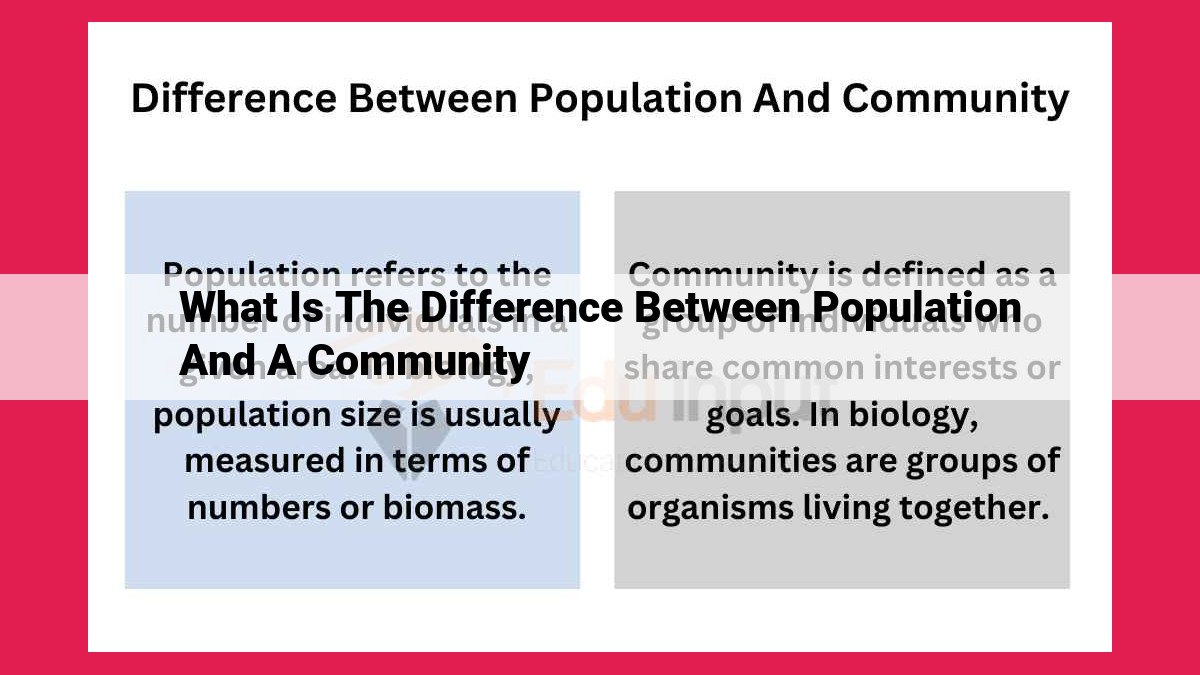
Populations, composed of individuals of a single species inhabiting a specific area, differ from communities, which encompass all species in that location. Communities, more complex than populations, are characterized by interactions between species and their environment, showcasing the intricate web of relationships that shape ecological systems. Understanding population dynamics and community structure is essential for unraveling the dynamics of ecosystems and the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth.
Population and Community: The Building Blocks of Ecological Systems
In the vast tapestry of nature, intricate connections weave together diverse species, shaping the communities they inhabit. Understanding these connections begins by deciphering the fundamental concepts of population and community.
A Population: A Unity of Life
Picture a vibrant crowd, each individual possessing unique traits that blend into a collective identity. This is the essence of a population, a group of organisms of the same species that live in the same area. Within this gathering, members interact, compete for resources, and contribute to the group's overall dynamics.
A Community: A Symphony of Species
Now, imagine a broader tapestry, where multiple populations coexist in harmony, each playing a distinct role. This is the concept of a community, an assemblage of different species that interact in shared habitats. Like a symphony orchestra, each species contributes its own melody, blending with others to create a complex and
Distinguishing between populations and communities is crucial for unraveling the intricate web of life. Populations form the building blocks of ecological systems, while communities provide a framework for understanding the interplay of different species. Together, they paint a vibrant picture of how organisms shape and are shaped by their environment.
Population Dynamics: The Dance of Life and Numbers
In the intricate tapestry of life, populations play a pivotal role. Demography, the study of population dynamics, provides invaluable insights into the birth, death, and migration patterns that shape populations. This knowledge is essential for understanding the health and stability of ecosystems.
Carrying Capacity: Setting the Stage for Growth
Imagine a population of rabbits in a lush meadow. As their numbers increase, so too does their demand for resources such as food and water. Eventually, a threshold is reached known as carrying capacity, beyond which the environment can no longer sustain further growth. This limit is determined by factors such as resource availability, disease, and predation.
Niche: Finding Your Place in the World
Within the vast expanse of an ecosystem, each species occupies a unique niche, a specialized role that reduces competition for resources. Foxes, for instance, prey primarily on rodents, while hawks soar high above, focusing on birds. These niche adaptations allow multiple species to coexist harmoniously, reducing the risk of extinction.
Habitat: The Home of a Population
The physical surroundings of a population, its habitat, also play a crucial role in its success. Penguins thrive in the icy waters of Antarctica, while desert tortoises endure the arid conditions of the Sonoran Desert. By adapting to specific habitats, populations ensure their survival in diverse environments.
Population dynamics is a complex but fascinating interplay of birth rates, death rates, and resource availability. By understanding these dynamics, we gain a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth. From the smallest microbes to the largest mammals, populations are the building blocks of ecosystems, shaping their structure, function, and resilience.
Community Structure and Function
In the tapestry of life, communities emerge as vibrant and intricate mosaics of interacting species. A community comprises all living organisms that share a specific habitat and interact with one another. They form complex webs of relationships, shaped by factors such as competition, predation, and mutualism. Understanding community structure and function is crucial for unraveling the intricacies of ecological systems.
Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity, the variety of life forms within a community, plays a pivotal role in its stability and resilience. Each species occupies a unique niche, exploiting different resources and contributing to the overall ecosystem function. Diverse communities are more resistant to environmental disturbances and provide a range of ecosystem services, such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and water purification.
Ecological Succession
Over time, communities undergo gradual changes known as ecological succession. This dynamic process involves the sequential replacement of dominant species, driven by factors such as competition, climate, and disturbance. As one species gives way to another, the community's structure and function evolve, creating a rich and ever-changing tapestry of life.
Understanding Ecosystems and Interspecific Competition
Ecosystems: The Interplay of Communities
In the tapestry of nature, ecosystems emerge as intricate webs of life, encompassing diverse communities of organisms and their non-living environment. Envision a flourishing forest, where tall trees reach towards the sun, casting shadows upon a vibrant understory of shrubs and wildflowers. Or a tranquil lake, teeming with fish, amphibians, and aquatic plants. Each ecosystem is a dynamic system, where communities of interacting species form the building blocks.
Interspecific Competition: A Driving Force in Community Dynamics
Within these ecosystems, interspecific competition plays a pivotal role in shaping the fate of different species. This occurs when individuals from two or more species compete for the same limited resources, such as food, space, or mates. Like runners vying for the finish line, these competing species expend energy in their pursuit of survival.
The outcome of interspecific competition can profoundly impact community dynamics. In some cases, one species may outcompete the others, leading to its dominance within the ecosystem. For instance, in a grassland, a particular grass species may possess superior adaptations for nutrient acquisition, allowing it to outgrow its competitors and establish a monoculture.
Coexistence and Adaptation
However, nature is often more nuanced than simple dominance. Interspecific competition can also drive species to coexist by specializing in different niches. In the aforementioned forest, one tree species may occupy the canopy, while another thrives in the understory. This partitioning of resources allows both species to persist alongside each other.
Moreover, competition can also trigger evolutionary adaptations. Faced with intense competition for food, some species may evolve specialized feeding strategies or develop physical traits that make them better competitors for specific resources. In this way, interspecific competition can serve as a catalyst for diversification and the emergence of new species.
Ecosystems and interspecific competition are interconnected concepts that underscore the dynamic and competitive nature of ecological systems. By understanding these factors, we gain insights into the intricate balance and interdependence of life on Earth. From towering trees to microscopic organisms, each species plays a unique role within its community, contributing to the overall health and resilience of our planet's ecosystems.
Related Topics:
- Sergei Rachmaninoff: Death And Legacy Of A Musical Master
- Unveiling The Essence Of Elements: The Dynamic Trio Of Protons, Electrons, And Neutrons
- Unlocking The Secrets Of Monomial Degree: Its Significance In Polynomial Operations
- Optimizing Image Quality In Microscopy: Understanding Magnification And Resolution
- Mastering The Formula For Finding The First Term Of An Arithmetic Sequence: Essential For Real-World Applications